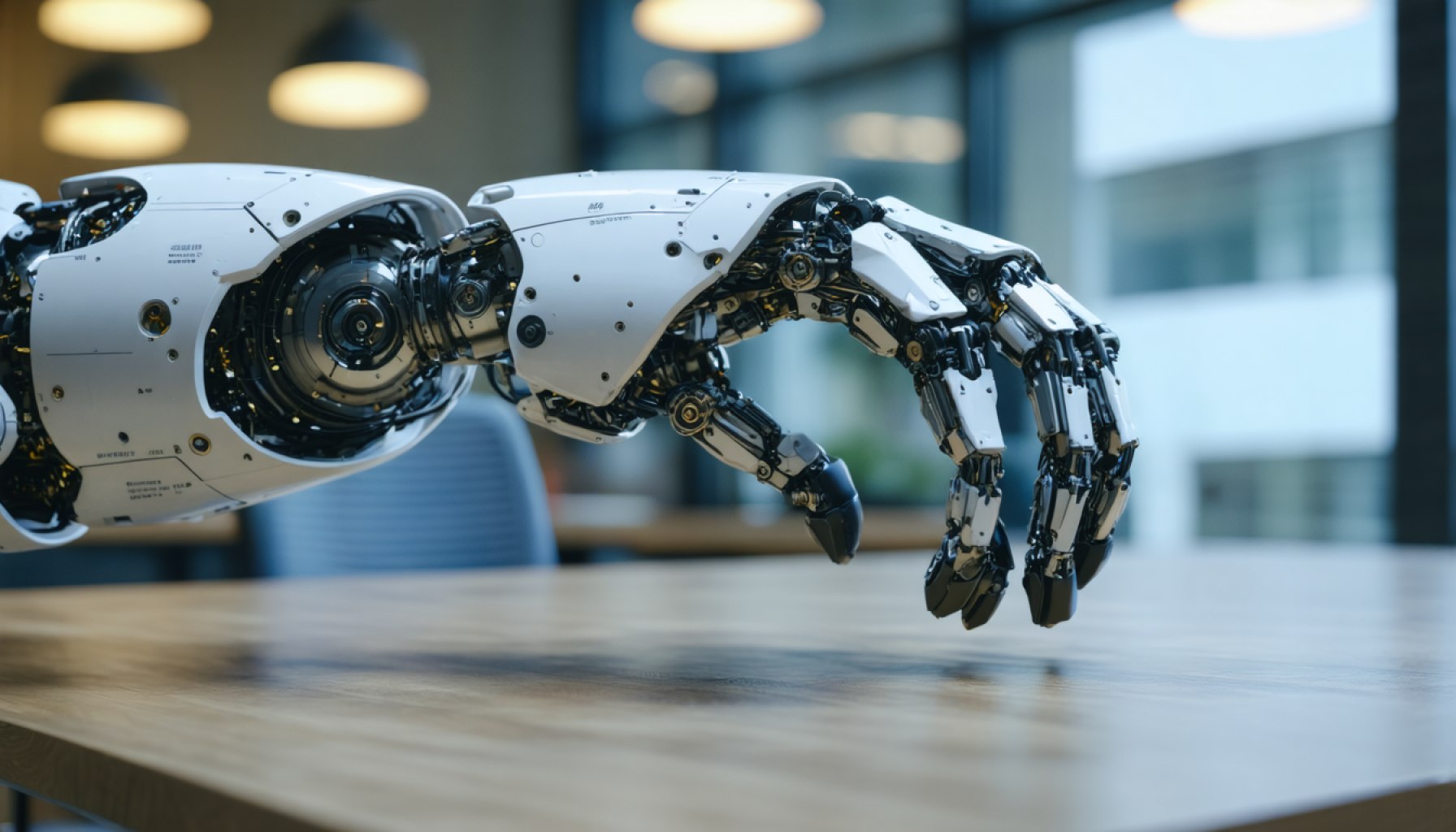
- The Assistive Dexterous Arm (ADA) is a cutting-edge robotic device developed by the University of Washington’s Personal Robotics Lab, designed to empower individuals with motor impairments.
- ADA is controlled via a mouth-operated joystick and equipped with sensors, facilitating independence in tasks like self-feeding.
- Jonathan Ko, a Seattle attorney, provides valuable feedback as both a user and a researcher, highlighting the importance of integrating real-world experiences into technological development.
- The ADA project emphasizes collaboration with individuals facing motor challenges, treating them as co-researchers and ensuring their voices influence the project’s direction.
- Under the leadership of innovators like Amal Nanavati, this initiative demonstrates that technology can enhance human connection rather than diminish it.
- The project underscores the transformative potential of technology rooted in empathy, envisaging a future where assistive devices offer empowerment and dignity.
A whir of servos hums in a Seattle kitchen where the scent of freshly toasted bread mingles with the creamy aroma of avocado. It’s breakfast time, yet something extraordinary is happening. A robotic arm, sleek and purposeful, delicately maneuvers a slice of avocado toast towards Jonathan Ko, a Seattle attorney. This isn’t just any day; it’s a groundbreaking collaboration between engineering innovation and human resilience.
For over a decade, the University of Washington’s Personal Robotics Lab has been at the forefront of developing the Assistive Dexterous Arm (ADA)—a marvel of modern robotics designed to grant autonomy to those with motor impairments. This ingenious device, brimming with sensors and guided by human input via a mouth-operated joystick, is revolutionizing the everyday task of self-feeding, a basic human experience that is often taken for granted.
Ko, who carries the unique perspective of a legal mind and an ADA community researcher, recently spent a week with ADA in his home. In doing so, he offered more than just physical space; he provided invaluable feedback that bridges the gap between complex technology and the subtleties of daily human need.
Across the landscape of assistive technologies, the lived experiences of people like Ko are frequently underrepresented, yet the ADA project is a refreshing exception. The UW robotics team has actively integrated insights from dozens of individuals facing similar challenges. They aren’t merely participants; they are co-researchers, shaping the course of robotic caregiving with their experiences and insights.
Under the enthusiastic guidance of innovators like Amal Nanavati, a fresh PhD graduate from UW’s Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science & Engineering, this venture breaks stereotypes about technology creating distance rather than connection. In this context, robots are not replacing human touch but rather augmenting it, weaving a new fabric of independence and dignity for those who need it most.
The key takeaway here is profound—technology, when developed with empathy and insight, transcends mere function. It becomes a lifeline, offering not just utility but empowerment. The ADA project is more than a gadget; it’s a testament to what’s possible when the human spirit meets the frontier of innovation. As Ko savors his avocado toast with ADA’s assistance, the vision of a world where such devices are commonplace becomes tantalizingly conceivable, drawing us closer to a future where technology truly serves humanity.
Revolutionary Robotics: Merging Human Dignity with Cutting-Edge Innovation
Introduction
The story of the Assistive Dexterous Arm (ADA) being used by Jonathan Ko, a Seattle attorney, offers a glimpse into how robotics can dramatically transform lives. The University of Washington’s Personal Robotics Lab has developed ADA, a sophisticated robotic arm aimed at enhancing autonomy for individuals with motor impairments. This remarkable technology not only illustrates the potential of empathetically developed robotics but also redefines the relationship between humans and machines.
Understanding ADA’s Impact in Daily Life
The Assistive Dexterous Arm (ADA) is equipped with sensors and is controlled through a mouth-operated joystick. This functionality allows users like Jonathan Ko to perform daily activities, such as eating, which many take for granted. ADA’s design and implementation can increase autonomy for individuals with motor impairments, bridging the gap between advanced robotics and daily human needs.
Key Features and Specs
– Sensors Integration: ADA includes an array of sensors that facilitate precision and safety in handling tasks like feeding.
– Human-Guided Interface: Operated via a mouth joystick, ADA emphasizes user control and tailoring to the individual’s physical capabilities.
– Adaptive Learning: The robotics team at UW ensures ADA evolves based on continuous user feedback, enhancing its functionality and user satisfaction.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
ADA’s functionality extends beyond Ko’s kitchen. Similar assistive technologies can be adapted for various environments:
– Elderly Care: Assisting seniors in living independently by aiding with tasks like eating, dressing, or even administering medication.
– Rehabilitation Centers: Offering innovative rehabilitation avenues for individuals recovering from strokes or other motor impairments.
– Independent Living: Empowering those with disabilities to achieve greater self-sufficiency in their daily lives.
Market Forecasts & Industry Trends
The assistive robotics market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. With increasing demand for devices promoting independence among individuals with disabilities and an aging global population, innovations like ADA are at the forefront. By 2025, the assistive robotics market is expected to exceed $3.9 billion, driven by technological advancements and increasing adoption.
Security & Sustainability
Ensuring the security and privacy of users is a top priority for assistive devices. Adhering to strict cybersecurity protocols to protect sensitive data and continuous updates to mitigate vulnerabilities are essential. Sustainability also plays a role—using eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies can lessen the environmental impact while ensuring ADA’s availability for the future.
Pros and Cons Overview
– Pros:
– Enhances autonomy and independence
– Provides personalized assistance
– Enables participation in daily life activities
– Cons:
– High initial cost and maintenance fees
– Requires integration and adaptation for different user needs
– Limited awareness and accessibility in the broader market
Conclusion & Recommendations
The development of ADA by the University of Washington’s Personal Robotics Lab demonstrates how technology, when intertwined with empathy and human insight, can facilitate independence and empowerment. As assistive technology continues to evolve, these innovations are set to become integral parts of daily life for many individuals.
Actionable Tips:
1. Awareness & Outreach: Raise awareness in communities about the potential of assistive technologies to foster broader adoption.
2. Collaboration: Encourage partnerships between technology developers and users to tailor devices that suit specific needs.
3. Investment in Research: Continue supporting research and development in assistive robotics to enhance functionalities and reduce costs.
For more information on similar innovations, visit the University of Washington.